考慮定向能量沉積工藝特點的減材加工余量優化(3)
時間:2022-10-13 11:08 來源:未知 作者:admin 閱讀:次
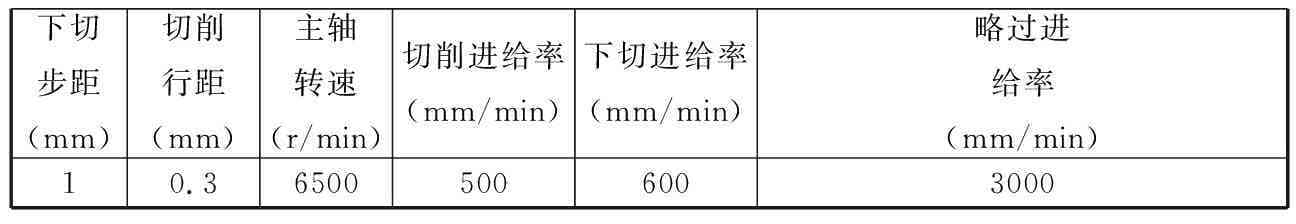
減材后處理的加工時間直觀體現配準效果對加工效率的影響。鑒于實際加工過程中裝夾、定位、換刀等輔助加工時間會影響實際有效加工時長的統計,故本文采用PowerMill仿真軟件對比了案例余量優化前后有效加工時長(包括進刀、退刀及銑削加工時間)。減材加工采用PowerMill葉片加工策略,粗加工至余量2 mm,并以粗加工時間表征優化前后加工效率。減材加工參數設置如表4所示。配準后模型粗加工相比配準前少加工兩道,時間縮短64 min 10 s,可見減材加工效率大幅度提高。
表4 PowerMill銑削粗加工仿真參數設置
2.4 驗證分析
2.4.1 不同檢測方案對余量優化影響
采用2.2節相同步驟優化以臺階效應波峰處測量點云為配準對象的加工余量,獲得變換矩陣對比組Rcon、Tcon:

(9)
圖15給出了對應余量優化結果,圖16為配準后余量分布云圖,可以看出余量分布相對均勻。圖17給出了對比組配準后余量直方圖信息,與圖13b實驗組配準結果相比,兩組數據呈正態曲線分布且趨勢相近,但對比組期望值μ更大,表明存在更多大余量區域。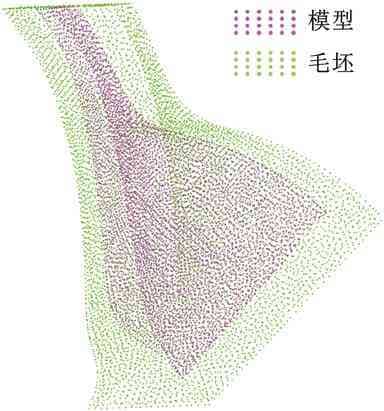
圖15 對比組余量優化結果
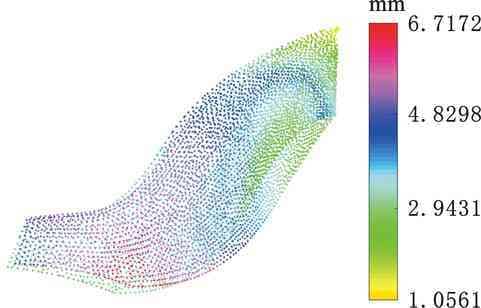
圖16 對比組余量云圖
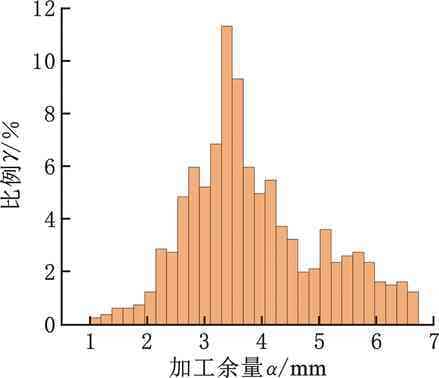
圖17 對比組余量統計直方圖
表5顯示,相對于波谷實驗組,波峰對比組余量均值dave增大0.3 mm,dmax增大0.89 mm。顯然,波谷測點構建的外輪廓體積比波峰測點小。采用波峰處最大外輪廓配準,可能造成配準后局部區域實際加工余量為零或負余量,導致毛坯報廢。另外,對比組S2值大于實驗組S2值,說明對比組測點余量均勻性差。根據實際成形效果觀測,制造凸起類缺陷(如局部黏附粉末、球化等)集中在波峰處。該類缺陷嚴重影響真實輪廓構建精度,進而影響余量優化結果。圖18顯示了DED毛坯上述缺陷。由于波峰處測點構建毛坯外輪廓更大,故理論粗加工多一道,時間增長31 min 28 s,實際最外層銑削僅接觸波峰與凸起類缺陷處,存在大量空刀路。因此,波谷處構建的截面線不僅能精確反映最小外輪廓,且可減少制造缺陷引起的非真實輪廓測點數量,更適用于減材余量優化。
表5 不同在機檢測方案余量統計結果
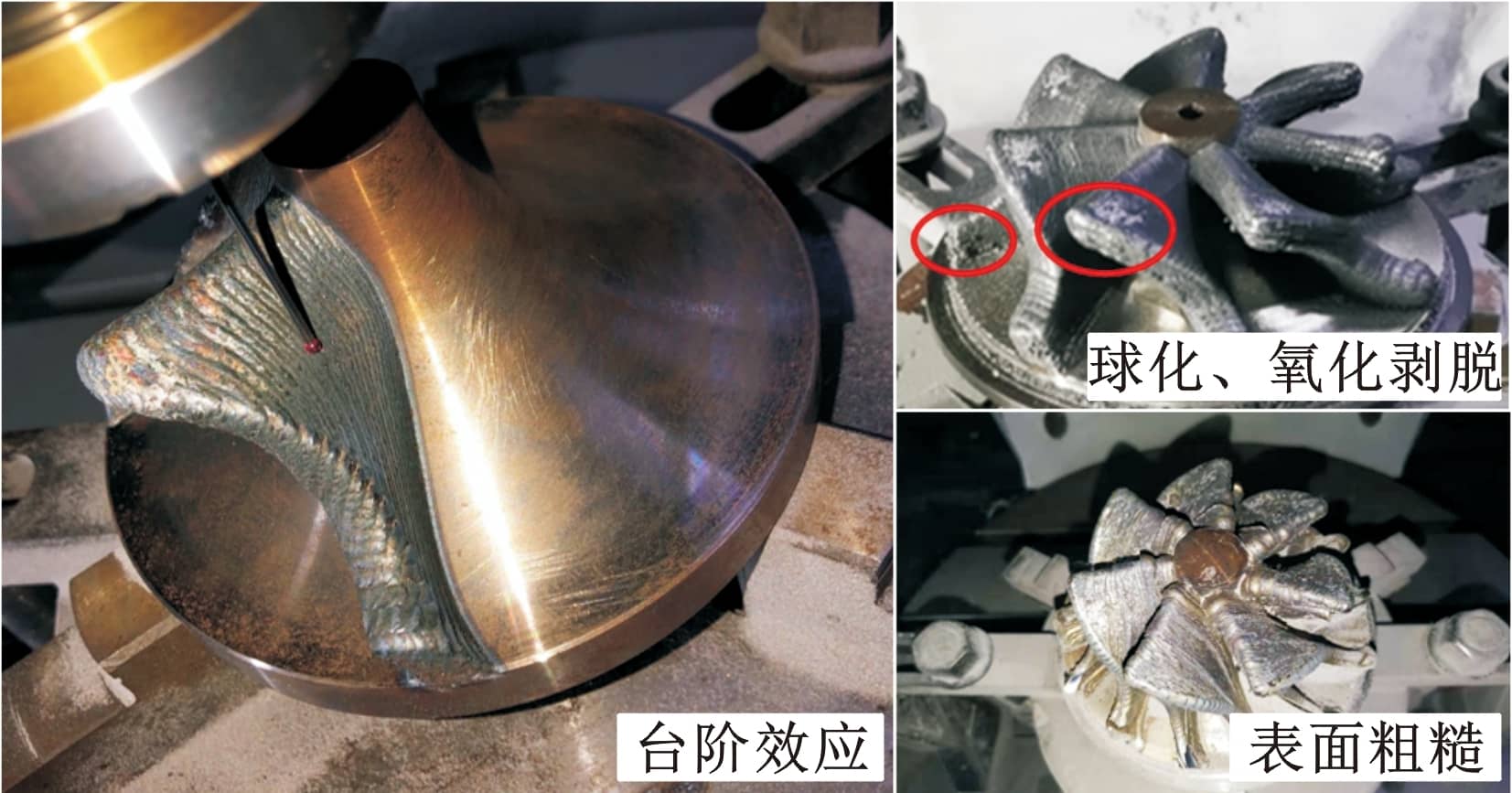
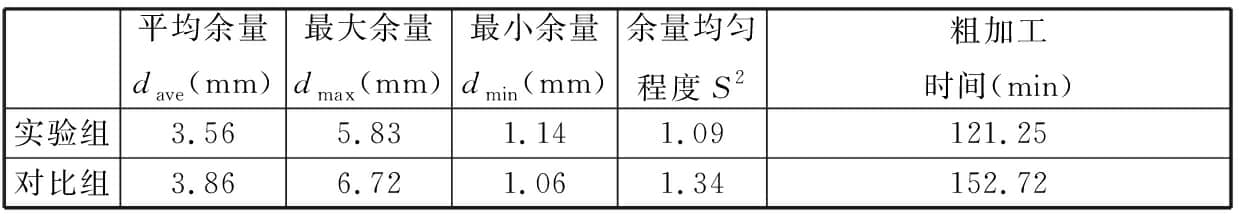

圖18 激光定向沉積制造精度
2.4.2 不同配準方法對余量優化的影響為進一步驗證本文所提余量優化算法的準確性,本節對比GAO等[16]提出的基于遺傳算法(genetic algorithm,GA)的加工余量優化方法。該方法綜合考慮了定位、均勻及外包絡原則,目標函數統一為
min fGA=alg(efix(R,T)+bexp(S2(R,T)+
cexp(1-P(D(R,T)
(10)
上式等號右邊三項分別對應定位、均勻及外包絡原則,a、b和c為確定的權重系數。本文重新定義權重系數a=0.2、b=0.4、c=0.9,余量優化結果如圖19與圖20所示。
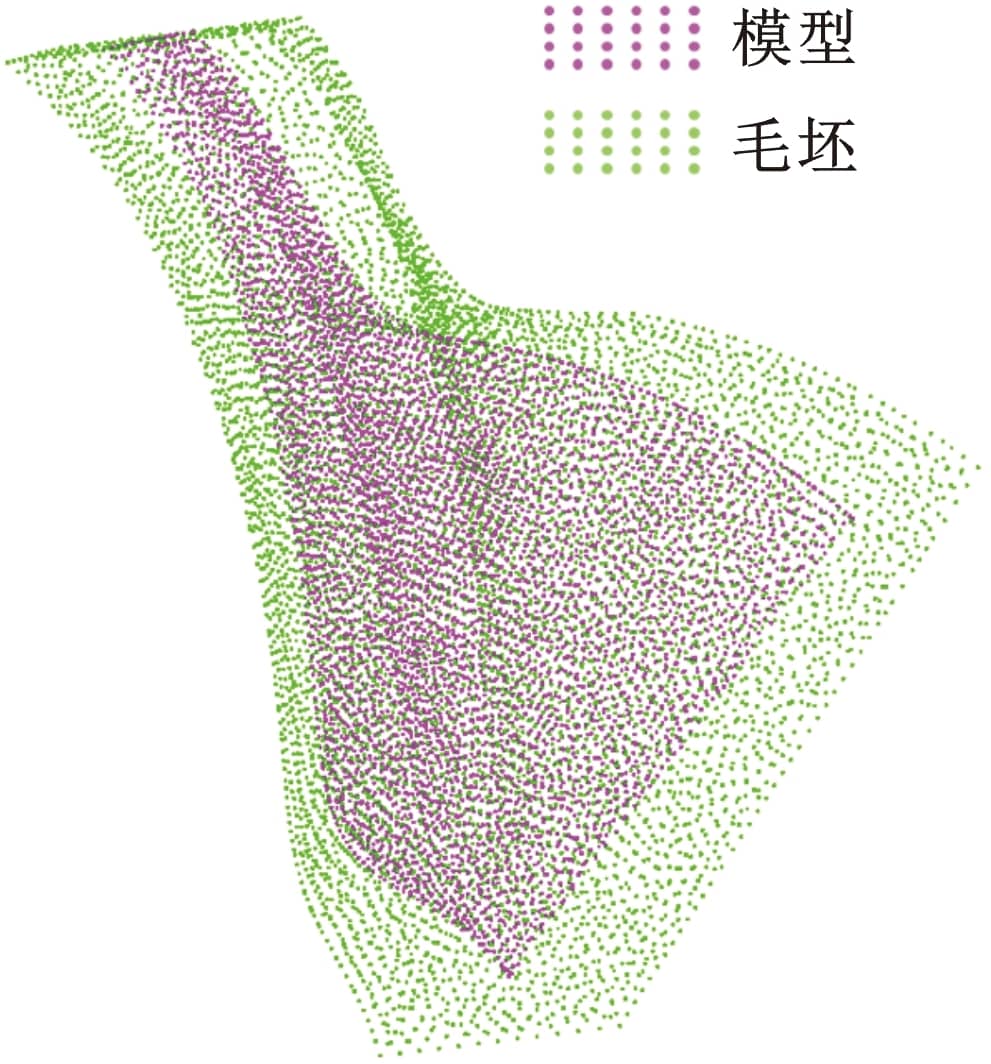
圖19 GA余量優化方法余量優化結果
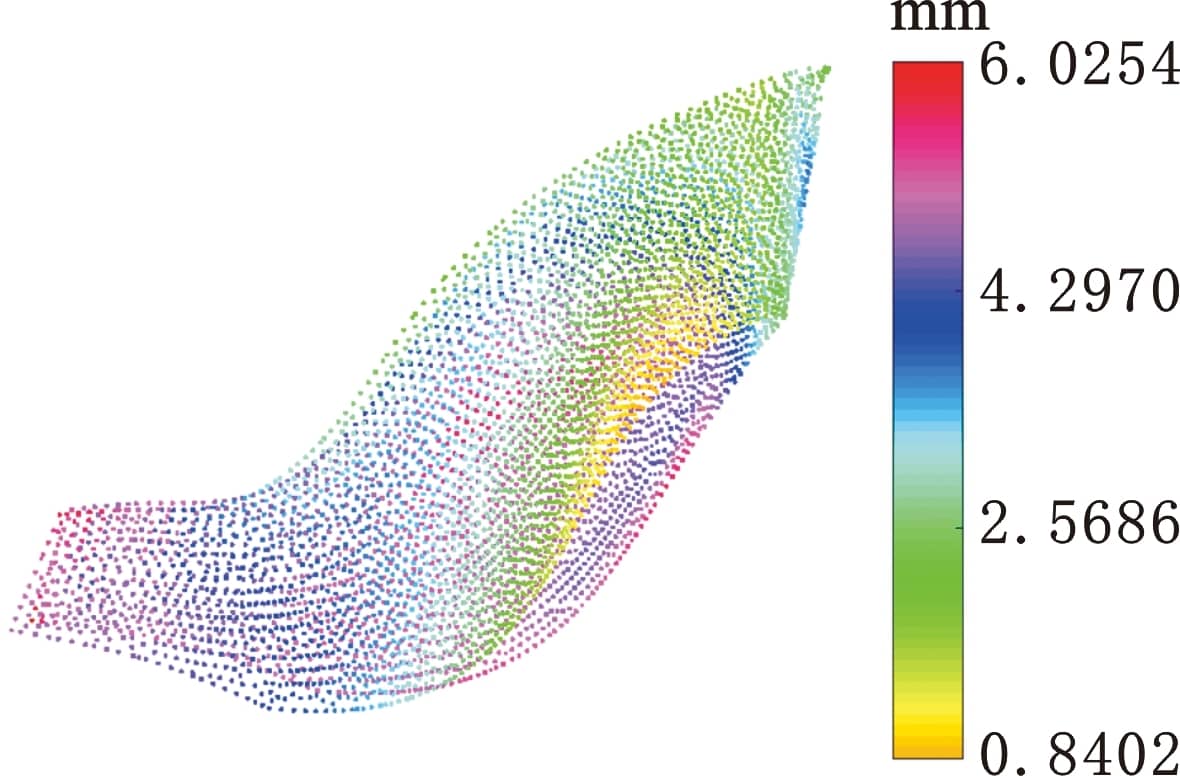
圖20 GA余量優化方法余量云圖
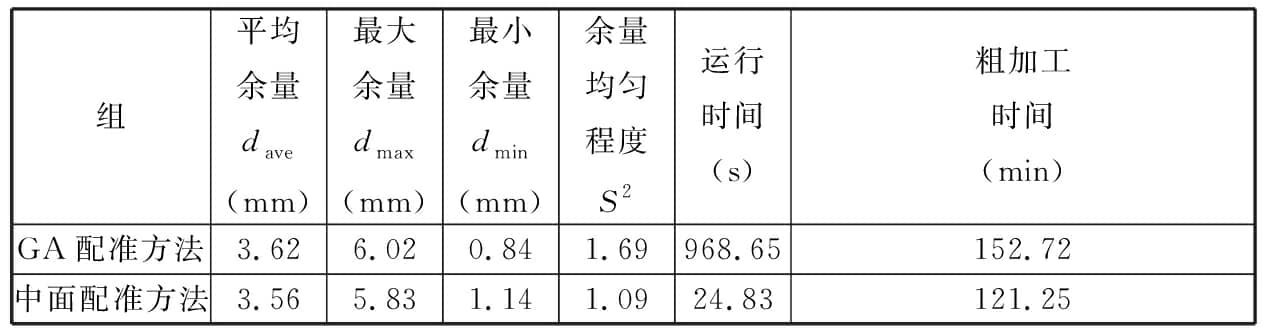
圖21為上述方法余量優化結果直方圖。相對于中面動態配準方法,GA優化后余量正態分布趨勢不明顯,效果不及所提方法。表6顯示,該方法所得余量平均值為3.62
mm、最大值為6.02 mm、最小值為0.84 mm、方差值為1.69。對比本文所提方法,平均余量僅相差0.06 mm,但最大余量增加0.19
mm,最小余量減少0.3
mm,配準后理論加工時間也更長,余量優化后的粗加工效率明顯不及所提方法。另外,需要指出,遺傳算法是模擬染色體交叉、變異等優化求解,運算周期較長,而中面動態配準方法,因減少了點云數量且不采用隨機求解,一般在幾十秒即可完成計算。綜上所述,所提方法綜合性能優于GA余量優化方法。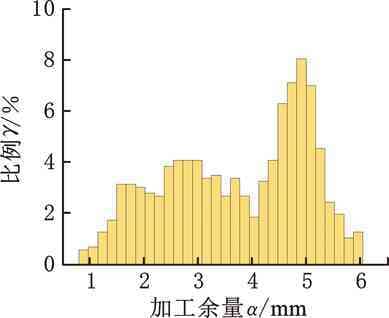
圖21 GA配準方法余量統計直方圖
表6 GA余量優化方法配準結果
3 結論
(1)所提在機檢測截面線構建方法考慮了曲面類零件DED制造產生的臺階效應,利用臺階效應波谷位置準確構建葉片最小外輪廓,避免測量由制造缺陷構成的非真實外輪廓。余量優化結果表明所提截面線構建方法給出更大最小余量dmin及更小余量方差S2,可避免DED近凈成形余量優化問題中局部余量不足現象。
(2)針對定位區域與待加工區域不同配準精度要求,引入動態權重因子平衡不同目標函數的博弈問題,同時,通過構造測量點云及理論模型點云中面,減少配準點云數量。相較于現有遺傳算法余量優化技術,所提方法顯著提高了余量優化效率。
(3)本文所提余量優化方法能快速優化DED毛坯與理論模型相對位置,均勻化減材加工后處理余量,可提高零件增減材復合加工效率并減小零件報廢率。后續減材規劃研究將進一步驗證和討論更復雜零件余量化后的效率提升效果。
參考文獻:
[1] LIU S, SHIN Y C. Additive Manufacturing of Ti6Al4V Alloy:a Review[J]. Materials and Design, 2019, 164:1-23.
[2] 顧冬冬, 張紅梅, 陳洪宇, 等. 航空航天高性能金屬材料構件激光增材制造[J]. 中國激光, 2020, 47(5):32-55.
GU Dongdong, ZHANG Hongmei, CHEN Hongyu, et al. Laser Additive Manufacturing of High-performance Metallic Aerospace Components[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5):32-55.
[3] DEBROY T, WEI H L, ZUBACK J S, et al. Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components-process, Structure and Properties[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2018, 92:112-224.
[4] KARUNAKARAN K P, SURYAKUMAR S, PUSHPA V, et al. Low Cost Integration of Additive and Subtractive Processes for Hybrid Layered Manufacturing[J]. Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2010, 26(5):490-499.
[5] MAYER T, BRNDLE G, SCHNENBERGER A, et al. Simulation and Validation of Residual Deformations in Additive Manufacturing of Metal Parts[J]. Heliyon, 2020, 6(5):e03987.
[6] BIKAS H, STAVROPOULOS P, CHRYSSOLOURIS G. Additive Manufacturing Methods and Modelling Approaches:a Critical Review[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 83(1/4):389-405.
[7] 曹著明, 孫紅梅, 史海軍. 某五軸數控加工中心在線檢測關鍵技術研究[J]. 機械設計與制造, 2017(11):149-152.
CAO Zhuming, SUN Hongmei, SHI Haijun. The Research on the Key Technology of On-line Inspectionof a Five-axis NC Machining Center[J]. Machinery Design and Manufacture, 2017(11):149-152.
[8] AHN D, KWEON J H, KWON S, et al. Representation of Surface Roughness in Fused Deposition Modeling[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Tech., 2009, 209(15/16):5593-5600.
[9] KAJI F, BARARI A. Evaluation of the Surface Roughness of Additive Manufacturing Parts Based on the Modelling of CUSP Geometry[J]. IFAC-Papers Online, 2015, 48(3):658-663.
[10] SHEN B, HUANG G Q, MAK K L, et al. A Best-fitting Algorithm for Optimal Location of Large-scale Blanks with Free-form Surfaces[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 139(1/3):310-314.
[11] LI X, LI W, JIANG H, et al. Automatic Evaluation of Machining Allowance of Precision Castings Based on Plane Features from 3D Point Cloud[J]. Computers in Industry, 2013, 64(9):1129-1137.
[12] SUN Y W, XU J T, GUO D M, et al. A Unified Localization Approach for Machining Allowance Optimization of Complex Curved Surfaces[J]. Precision Engineering, 2009, 33(4):516-523.
[13] 張瑩, 劉敏, 張定華, 等. 基于在線檢測的葉片加工余量自適應優化方法[J]. 計算機技術與發展, 2014, 24(11):226-229.
ZHANG Ying, LIU Min, ZHANG Dinghua, et al. An Adaptive Approach for Machining Allowance Balancing for Blade Based on Online Measurement[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2014, 24(11):226-229.
[14] YING Z, ZHANG D, WU B. An Approach for Machining Allowance Optimization of Complex Parts with Integrated Structure[J]. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 2015, 2(4):248-252.
[15] 張明德, 馬帥, 謝樂, 等. 大型船用螺旋槳自適應加工方法研究[J]. 機械科學與技術, 2019, 38(11):1752-1759.
ZHANG Mingde, MA Shuai, XIE Le, et al. Study on Adaptive Machining Method for Large Marine Propeller[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2019, 38(11):1752-1759.
[16] GAO Y Z, DU Z J, LI M Y, et al. An Automated Approach for Machining Allowance Evaluation of Casting Parts[J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2019, 32(11):1043-1052.
[17] 岳晶. 整體葉輪在機檢測與加工余量優化技術研究[D]. 武漢:華中科技大學, 2016.
YUE Jing. Research on On-machine Measuring and Allowance Optimization Technology of the Integral Impeller[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2016.
[18] 譚高山, 張濤, 張麗艷, 等. 基于動態精度評估機制的自適應定位方法[J]. 計算機集成制造系統, 2021, 27(12):3550-3558.
TAN Gaoshan, ZHANG Tao, ZHANG Liyan, et al. Adaptive Localization Method Based on Dynamic Accuracy Assessment Mechanism[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 27(12):3550-3558.
[19] 王威振, 莫蓉, 萬能. 葉片模型公差約束條件下的配準方法研究[J]. 計算機工程與應用, 2013, 49(10):264-266.
WANG Zhenwei, MO Rong, WAN Neng. Tolerance Zone Constrained Registration Method for Aeroengine Blade Models[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2013, 49(10):264-266.
[20] BESL P J, MCKAY N D. A Method for Registration of 3-D Shapes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(2):239-256.
[21] 劉宇, 熊有倫. 基于有界K-D樹的最近點搜索算法[J]. 華中科技大學學報(自然科學版), 2008, 36(7):73-76.
LIU Yu, XIONG Youlun. Algorithm for Searching Nearest-neighbor Based on the Bounded K-D Tree[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(7):73-76.
[22] ARUN K S, HUANG T S, BLOSTEIN S D. Least-squares Fitting of Two 3-D Point Sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1987, 9(5):689-700.
[23] 孔劉偉, 王振忠, 葉超, 等. 五軸增減材混合加工中心集成開發技術研究[J]. 航空制造技術, 2019, 62(6):53-59.
KONG Liuwei, WANG Zhenzhong, YE Chao, et al. Research on Developing Technology of Five-axis Additive-subtractive Hybrid Machining Center[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 62(6):53-59.
Subtractive Post-machining Allowance Optimization Considering Characteristics of DEDs
HOU Liang GUO Jing CHEN Yun YE Chao XU Yang ZOU Jiahao
Department of Mechanical and Electric Engineering,Xiamen University,Xiamen,Fujian,361005
Abstract: Complex free-form parts manufactured by DED had problems of uneven allowance distributions and severe stair-case effects. In order to optimize allowances for subtractive post-machining, a dynamic point cloud registration method using the mid-surface points of the deposited and theoretical parts was proposed to optimize the machining allowances, which took into consideration characteristics of the DED parts. Firstly, the section line of the minimum outer envelope of deposited complex free-form parts was constructed according to the deposition scanning path, and was used for obtaining the point cloud of the on-machine measurement. Secondly, the mid-surface points of the deposited and theoretical parts were extracted, and an iterative closest point with dynamic weights considering the multi-region allowance requirements was proposed to optimize the machining allowances. The feasibility of the algorithm was verified by two simple cases. Finally, a free-form blade of a centrifugal impeller was selected as a complex case for allowance optimization. The proposed method was also compared with the method for multi-region allowance using genetic algorithm. The results show that the proposed allowance optimization method is more accurate and efficient for rapid optimization of machining allowances for DED manufactured complex curved parts.
Key words: directed energy deposition(DED); allowance optimization; on-machine measurement; dynamic registration; stair-case effect
作者簡介:侯 亮,男,1974年生,教授、博士研究生導師。研究方向為大批量個性化定制和增減復合制造等。發表論文197篇。E-mail:hliang@xmu.edu.cn。陳 云(通信作者),女,1987年生,助理教授。研究方向為增減復合制造、難加工材料切削機理、精密檢測等。發表論文21篇。E-mail:yun.chen@xmu.edu.cn。
(責任編輯:admin)
最新內容
熱點內容


 NASA與ICON聯手推進太空3D
NASA與ICON聯手推進太空3D 第八屆醫院3D打印論壇:個
第八屆醫院3D打印論壇:個 3D打印巨頭Stratasys收購
3D打印巨頭Stratasys收購 Nature子刊:3D打印技術助
Nature子刊:3D打印技術助 全球兩大3D掃描儀巨頭合并
全球兩大3D掃描儀巨頭合并 美國交通部長稱,FAA正借
美國交通部長稱,FAA正借 美國空軍2860萬美
美國空軍2860萬美 美國軍工企業強強
美國軍工企業強強 美國斥資450萬美
美國斥資450萬美 GoEngineer通過收
GoEngineer通過收 3D食品打印:烹
3D食品打印:烹 卡內基梅隆研究人
卡內基梅隆研究人

